After several posts on the Big Data implementation process, let’s look at the ways Big Data can be used by your organization.
The following is copied from the Datafloq website, which provides many great articles on Big Data implementation. I highly recommend subscribing to their newsletter.
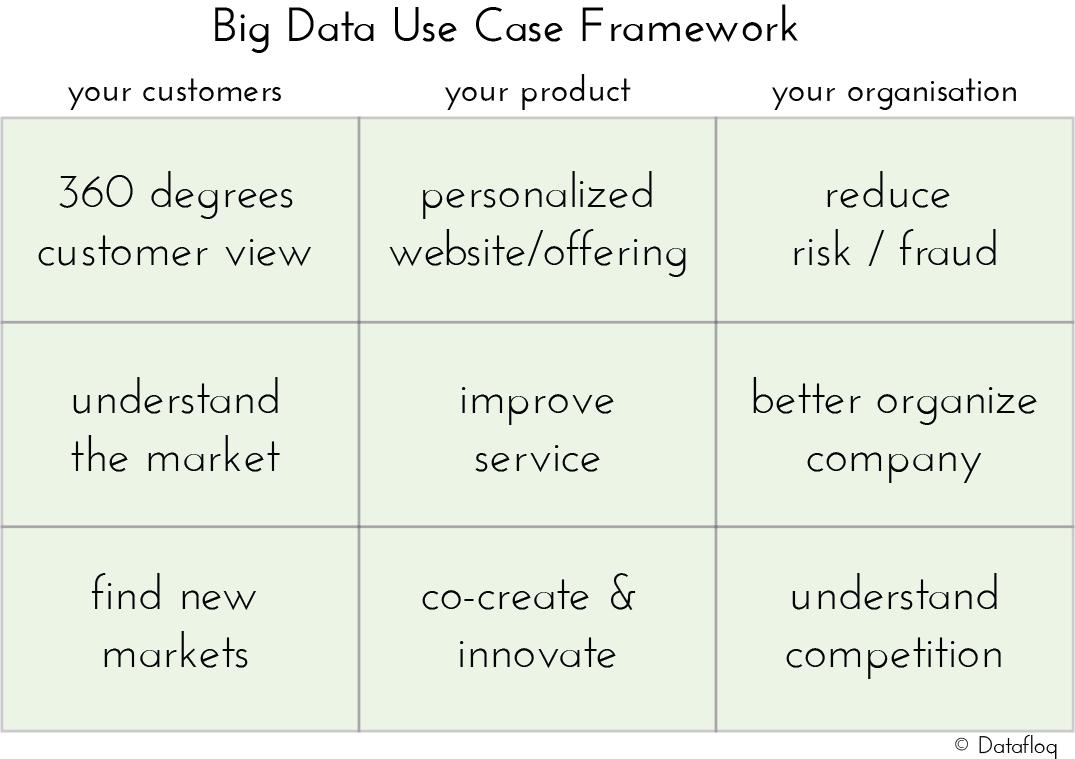
9 Generic Big Data Use Cases to Apply in Your Organization
(reposted from DataFloq)
Big Data means something different for every organization and every industry. What Big Data can do for your organization depends on the type of company, the amount of data that you have, the industry that you are in and a whole lot of other variables. Whenever I advise organization on their Big Data strategy, this is the main problem; there are so many different possibilities and often it is a struggle to find the right use case to develop into a Proof of Concept. That’s why I have developed the Big Data Use Case framework, to help organizations understand the different possibilities of Big Data and what it can do for their business. The framework divides 9 generic Big Data use cases into three different pillars:
- Your Customers;
- Your Product;
- Your Organization.
For each pillar there are three Big Data use cases that can be defined, which are relevant for all organizations across all industries. The framework looks as follows and let’s discuss the Big Data use cases one by one:
360 Degrees Customer View
Developing a complete view of your customer is important for every organization, as it helps to understand what your customer wants, what the needs and preferences are and how the customer has to be approached. When you combine multiple data sources you can get a 360 degrees overview. Your internal sources such as your CRM data, sales data or call centre data can be combined with external sources such as social media data or news data. The retailer Walmart is the best example of creating 360 degrees customer profile. Thanks to their online marketing platform, they are capable of creating segments of 1.
Understand The Market
When organizations want to gain a better understanding of the market, they traditionally turn to market research organizations. Consumer panels, focus groups and questionnaires provide insights in what the market thinks, but unfortunately it is time-consuming, expensive and always offers insights from the past instead of the future. With Big Data this is not necessary anymore. When you mix different data sets such as sales data, market news data and social media data, you can get real-time insights what the market thinks of your product and when you launch for example a new commercial, you can get insights in real-time how it is perceived. Big Data brings market research to the next level.
Find New Markets
Analysing various data sources such as web statistics and social media can help you find new markets or customers with latent needs that you were not aware of. Using techniques such as Natural Language Processing or Machine-Learning you will be able to better anticipate what (potential) customers are looking for and pattern analytics can result in finding completely new markets.
Personalized Website / Offering
Big Data is all about relevancy and offering the right product/service to the right person for the right price via the right channel at the right moment in time. Google personalizes its search results based on your profile and Amazon offers different homepages, with different products on offering, to almost each visitor. It comes back to completely knowing your customer by combining different data sources to really know what they are looking for. There are ample examples of companies successfully targeting their customers with personalized products including the InterContinental Hotel Groupand Spotify.
Improve Service
Big Data enables you to drastically improve your service. Using deep data analytics, you can optimize your customer service, resulting in happier customers. A great example of this practice is Southwest Airlines; they use speech analytics to extract in real-time deep and meaningful information out of live-recorded interactions between staff and customers. This data, combined with other sources such as customer profiles, flight information and social media data enables their staff to offer consistent high-quality service.
Also smart cities can use Big Data to better organize their cities and improve the service towards citizens. The smart city of Songdo is a great example, where even garbage is analyzed in order to improve the garbage removal services.
Co-create and Innovate
Big Data not only provides your insights about your customers, but can also give you information regarding the products and how these are being used. When you are capable of monitoring how the product is being used via sensors and telematics, you gain a deep understanding of how you can improve the product. In addition, simulation analysis using massive amounts of data and supercomputers will enable you to drastically speed-up the innovation of your products. As a result, P&G used simulation analytics to create thousands of iterations in seconds in order to find the best disposable diaper.
Reduce Risk / Fraud
Anomalies and outliers can easily be detected with Big Data and these anomalies and outliers could indicate fraudulent actions. MasterCard uses Big Data to determine during the payment process whether or not a certain payment is legitimate or fraudulent. In addition, Big Data can also reduce the risk you are facing. When you have a better understanding of your customer, you can better determine their risk profile (whether it is a customer or a business looking for a credit, mortgage or insurance). English car insurer Insurethebox is a pioneer in reducing risk by allowing customers voluntarily to have their driving habits monitored. The better they drive, the lower their insurance fee. Of course this also reduces the risk for the company.
Better Organize Your Company
Employees generate massive amounts of data at the office. Sensors installed on office furniture and throughout the office can provide insights in how employees behave at work. These insights can be used to better organize the workplace. Cubist Pharmaceuticals for examples, used data to reveal it had too many coffee machines. By reducing the amount of coffee machines and creating centralized coffee spots, they increased serendipitous interactions among employees.
You can also monitor all the unstructured data such as emails, documents and meetings to know which employee is knowledgeable about what topic and which employees interact with each other. This should not be seen as spying on your employees, but will help employees to find the information they need faster and more efficient.
Understand Your Competition
Of course, what you can do for your own organization, can also be done, more or less, for your competitors. When you monitor the pricing strategy of your competitor, Big Data can inform you in real-time when they adjust pricing, allowing you to responds faster. Of course, this strategy is not completely without risks as when two algorithms start interacting, strange things can happen; such as a book about flies for sale for over $ 23 million.
These nine Big Data use cases are just the tip of the iceberg of what is possible with Big Data. Of course, specific use cases differ per organization and industry, but hopefully this framework provides some guidance in how you can start with Big Data.